Did your gynecologist use the word cervical cancer, and that scared you? Are you unaware of the Big terms used by your doctor? Well, calm down! We will cover everything about cervical cancer in detail.
Did you know according to an estimated study about cervical cancer, around 14 thousand women will be affected by cancer in 2021 in the US alone?
Isn’t that a big number? Well, thankfully, the figure is much lower than in the past.
Yes! You heard it right! The number of cervical cancer cases from the past 40 years has declined tremendously. All because of the new approaches to finding cancer at the earliest possible stage.
What does cervical cancer mean? What are the high-risk factors of cervix cancer? How can you prevent it? Let’s clear your queries one by one!
What Is Cervical Cancer?
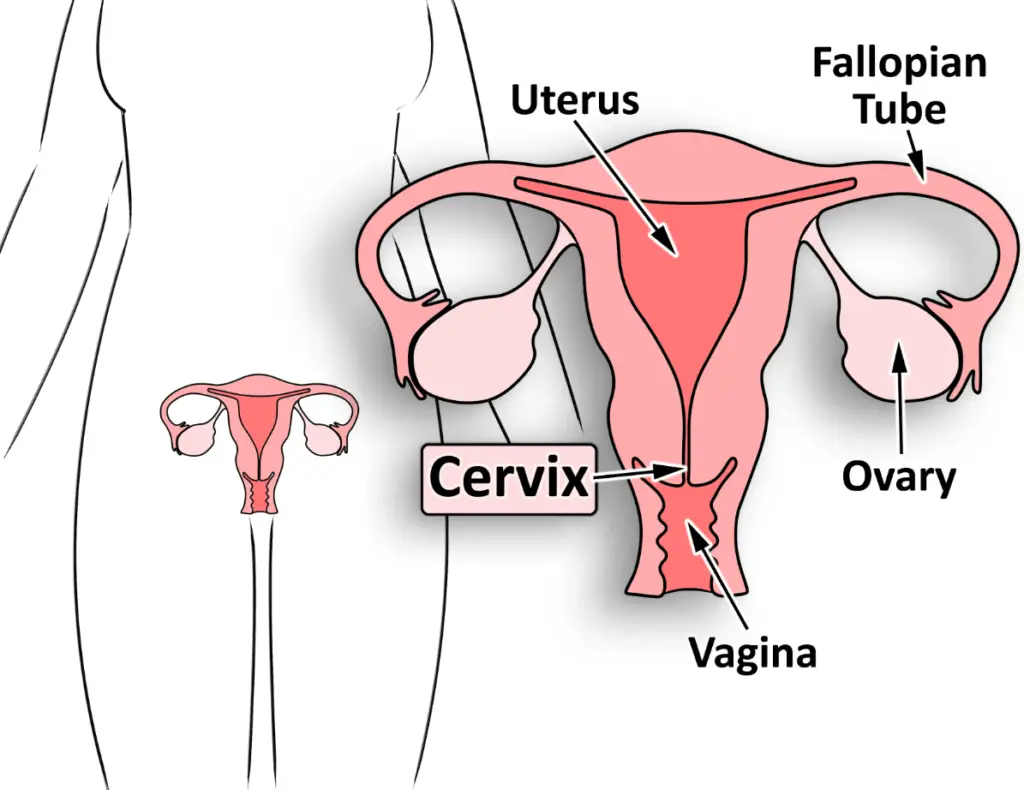
To make it easy for you, remember that the word cervical arose from the word cervix. This means that cervical cancer is the cancer of the cervix. Now, what is the cervix?
Cervix is the part of a reproductive organ in females that joins the uterus inside, with the vagina outside. Now any abnormal cellular changes in this part will lead to cancer.
Mind you: when we say any, it doesn’t mean that all types of changes in the cervix lead to cancer. NO! In fact, the cervix grows with age. And especially during the reproductive age and pregnancy, you will notice massive changes in the cervix. But that is not cancer.
But how would you differentiate between normal and abnormal cervix? Well, to know that, you need to know the signs and symptoms of cervical cancer first.
And once you have read them all, ask yourself; am I experiencing any of these symptoms? If yes, then call your doctor. If your answer is negative, good news; you are well and fine!
Signs and Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
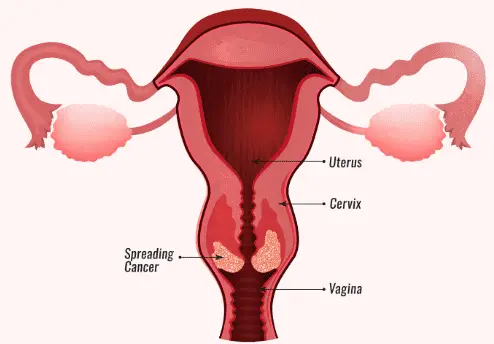
Signs and symptoms of cervical cancer are variable. This means that as cancer progresses to advanced stages, the symptoms become worse.
Note: Observe your monthly cycle, sexual activity, and any unusual change in the abdomen to diagnose cancer at an early stage.
In early-stage
It’s sad to know that during the pre-cancerous or early stage of cervical cancer there are no significant symptoms.
There is no pain, no discharge, nothing to rule out the probability of cancer. This is why every woman needs to have a regular pelvic checkup after the age of 21 years.
Noticeable symptoms in late-stage
In the advanced stage of cervical cancer, that is, when cancer has developed enough to produce the symptoms, you might experience the following symptoms:
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Abnormal bleeding after sexual contact
- Heavy periods lasting for more than a week
- Inter menstrual bleeding (bleeding between the monthly cycles)
- Vaginal bleeding after menopause
- Unusual discharge from vagina with a foul odor
After the cancer has metastasized
This is the most advanced and deadly stage of cancer. Once cancer has spread to the other organs of the body, you will notice symptoms unrelated to the functions of the cervix or uterus. For instance;
- Cancer might invade the bladder, which will result in difficulty or pain during urination.
- You might as well see blood in the urine.
- If the rectum is involved, it would be painful to defecate, and diarrhea may occur.
- In even severe cases, bleeding from the rectum ensues.
- Back pain or swelling in the lower limb (legs).
- Generalized symptoms like; weakness, weight loss, nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain, and swelling are common.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
Now that we know how cervical cancer expresses itself in a female’s body, the next question is, what is the cause of this cervical cancer? And from where does all of this start? Let’s find out!
Every cancer in any part of the body is caused by mutations or abnormal changes in our DNA. And the same goes for cervical cancer.
But what is DNA? It is that part of our system which helps us identify each other individually. In simple words, DNA has millions of genes that separate one organism from another.
Now the point to note is, any mutation in these genes will change the normal anatomy and physiology of a human being. As a result of this, a person suffers from various diseases. And that is exactly what happens in cervical cancer.
What Is HPV?
So, the most common cause of cervical cancer is the Human Papillomavirus. This virus is transmitted through sexual contact. It has around 100 viral types, all of them causing different kinds of diseases in different parts of the body.
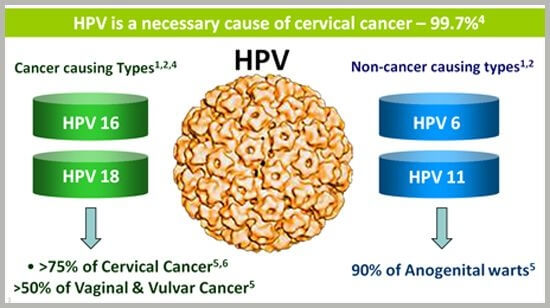
Human papilloma is known for causing genital warts. Mainly, the two genes HPV 16 and 18, are responsible for cervical cancer.
Plus, apart from infecting the cervix, it can also affect the vagina, anus, penis, rectum, and throat, where it causes cancer of the named parts.
Now, what does it exactly do after reaching the cervix? How does HPV bring such vast changes in the cervix that leads to cervical cancer? Read carefully;
Normally, there are two sets of genes in our body:
- Oncogenes, responsible for cell growth.
- Tumor suppressor genes suppress cellular growth to prevent abnormal cell division.
Human Papilloma Virus inhibits the function of suppressor genes by mutation, due to which the oncogenes keep on forming abnormal cells. Thus, leading to cervical cancer.
Types of Cervical Cancer
There are two types of cervical cancer based on its location and spread:
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
This is the commonest type of cervical cancer. And around 90% of women with cervical cancer have squamous cell carcinoma.
In this type, the cancer is located in the exocervix part close to the vagina because that is where the squamous cells are located.
Adenocarcinoma
The second common type is Adenocarcinoma. In this type, the cancer is in the endocervical (glandular) part of the cervix. This part is in direct association with the uterus, so the cancer can travel and spread to the uterus.
Mixed State
In this type, as the name discloses, the patient has symptoms and the appearance of both types of cancers.
Stages of Cervical Cancer
Like any other cancer of the body, cervical cancer has stages that help patients with the necessary treatment corresponding with that stage.
Now the rule of thumb is, the more advanced the stage is, the harder it gets to treat the patient.
So it is better to get the treatment as soon as possible to avoid further complications. Anyway, there are four stages of cervical cancer:
- Stage I: The cancer is localized in the cervical tissue only. There is no metastasis.
- Stage II: In this stage, the tumor grows bigger and crosses the cervix.
- Stage III: The cancer spreads to the nearby organs and lymph nodes, but not too far in the body.
- Stage IV: The last stage is the worst of all. At this point, the cancer has spread to the deeper tissues, lymph nodes, and distant organs like the lung, liver, and kidney.
Cervical Cancer Risk Factors
Cervical cancers most commonly occur in women of age 30 to 40 years. And it is unlikely for females below 20 years of age to develop this type of cancer.
However, it is recommended that as a woman turns 21, she should have routine screening tests to detect the cancer at an early or pre-cancer stage.
Moving on, let’s discuss the major risk factors leading to cervical cancer in females.
Modifiable risk factors
These are the factors that can be modified by changing lifestyle. And it is better that you take notes and avoid the risk of having cervical cancer.
- Multiple sexual partners
- Sexual contact at an early age (before 18 years)
- In pregnancy, due to a weakened immune system. Plus, the women who had three full-term pregnancies in the past are at higher risk of developing cervical cancer.
- A poor immune system like in HIV patients. And in the people who are taking immunosuppressive medications.
- Smoking
- A poor diet deficient in fruits and vegetables.
- Oral contraceptive pills
Non-modifiable risk factors
These factors bring a piece of bad news with them as they are not under our control. But luckily, there aren’t many factors that can’t be modified.
- Family history: If your mother, aunt, or grandmother has a history of cervical cancer, chances are you will get it as well in the near future. However, taking precautions and regular pelvic examination can help diagnose the cancer earlier. And you can start with the treatment sooner.
- Diethylstilbestrol (DES): It is a hormonal drug used by females in the 19th Century to prevent miscarriages. However, the drug was discontinued because of its deadly risk of producing cervical cancer.
However, remember that not every female with these risk factors gets cervical cancer. Well, that’s good news. But it is always better to get yourself tested and consult with a doctor.
Diagnostic Tests for Cervical Cancer
Living in the 21st Century, we are lucky to have many medical approaches available to screen for cancer and diagnose it sooner. For screening, the two tests are;
Pap Smear
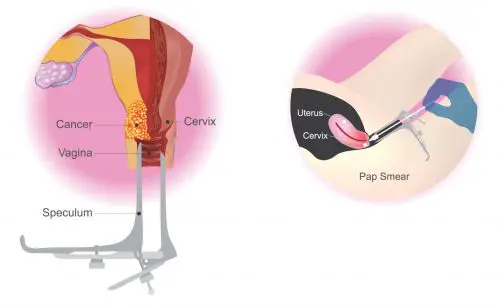
Pap test is the ideal and preferred test to screen for cervical cancer. It suggests the bizarre changes in cervical tissue at any point. Therefore, every female should get her pap smear done after every three years after turning 21.
To prepare you for the pap test, your doctor would ask you to avoid any sexual contact, vaginal sprays, or creams for 48 hours.
This is because doing any of these might inflame the cervical tissue giving you positive results, while in reality, you might not have cervical cancer at all.
HPV Test
HPV DNA Test is another method to diagnose cancer at an early stage. In this test, the doctors check the cervix for possible HPV infection, which is the most common cause of cervical cancer.
In both tests, your doctor will scrape off some cervical tissue and send them to the lab for examination.
Note: Not every Pap or HPV test that is positive means you have cervical cancer!
On the other hand, if your tests are positive, your doctor will perform a routine Pelvic Examination to check on the cancer progress.
Furthermore, there are other alternative methods to diagnose cancer.
- Colposcopy; to closely examine the cervix or vagina using a colposcope.
- Punch Biopsy; to scrape off the cervical tissue using a sharp tool.
- Endocervical curettage; is the same as punch biopsy, only that it is done using a spoon-shaped instrument or brush.
- Biopsy is helpful in further confirming the presence and spread of cancer.
- Imaging tests and Cystoscopy help in finding out the spread of cancer to other organs.
Cervical Cancer Treatment
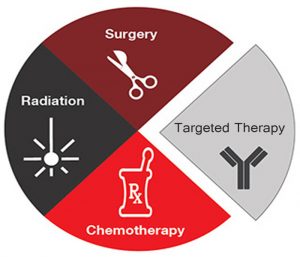
Can cervical cancer be treated? Of course it can!
However, the treatment and prognosis depend upon the stage and spread of cancer. Let’s discuss the options to treat cervical cancer:
Surgery
Cervical surgery is most effective in treating the cancer. However, the type of surgery you require depends on your stage of cancer.
- In the early or precancer stage, the cancerous cervix is removed by conization. In this process, the doctors take out a cone-shaped piece of cervical tissue mostly from the transformation zone. Now note that, in cone biopsy, there is the removal of the cells of the cervix only, which means the uterus and surrounding tissue is still intact so there won’t be any serious side effects.
- In the Invasive stage, simple hysterectomy or trachelectomy (removal of the cervix) are the two processes done depending on the size of the invasion.
- The advanced stage of cancer requires complete or radical hysterectomy, that is, the removal of the uterus, cervix, vagina, and surrounding lymph nodes and ligament. However, after this treatment, it is hard to get pregnant as there is no uterus left to conceive the baby.
Radiation Therapy
Treatment with radiation is usually done after surgery when there are high chances of cancer returning after the treatment. The high energy X-rays used in radiation therapy kill the cancerous cell.
It can be done externally from outside the body or internally by passing a radioactive tube through the vagina.
- External beam radiation: This therapy is performed like a normal X-ray. In this process, the beams are focused on the cancerous site from outside the body to kill the abnormal cells.
- Brachytherapy: Also known as Internal Radiation Therapy, in which a small device is fixed inside the vagina for a few minutes. This device directs the X-rays to the affected cells and kills them.
Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy is sometimes performed with chemotherapy, a procedure known as Concurrent Chemoradiation.
Chemotherapy is useful when the cancer has metastasized to distant organs. In this treatment, the doctors inject certain drugs into the veins that travel to the cancerous organ to kill the cancer cells. Drugs like Cisplatin, Fluorouracil, Topotecan, and many others are used in chemotherapy.
Targeted Drug Therapy
For advanced stages of cancer, localized drug treatment is useful to stop the blood vessels from growing. As a result, the cancer cells will have no nutrients to survive, and eventually, they will die.
For example, Avastin (Bevacizumab) is a drug used to inhibit the formation of blood vessels. This drug is given alongside chemo.
However, once the treatment starts showing some progress and the cancer regresses, chemo is stopped and the patient is kept on targeted drugs only.
Immunotherapy
Cancer cells can remain unnoticed in the body, hence our host defense might not be able to fight them. But not anymore!
Thanks to the researchers who were able to develop a medicine that can stimulate the patient’s immune system and helps destroy the cancerous tissues in a process called immunotherapy.
Prevention of Cervical Cancer
It is always better to be precautious than to regret it later.
Following are the preventive measures to save yourself from getting cervical cancer:
- Routine pap test
- Receive HPV vaccine if possible
- Limit the sexual partners and activity
- Have safe sex (use condoms)
- Stop smoking
FAQs
Yes, if it gets diagnosed early. And No, if you are in the last stage of cancer. In fact, no cancer in its advanced stage ever goes away.
Surgery is the best and safest treatment of cancer in pregnant women. On the other hand, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are highly contraindicated during pregnancy.
Conclusion
So that was everything about cervical cancer that you all need to know. Clearly, if you forget to keep a regular check on your reproductive health, you will be in great trouble. Plus, the sooner you find out about the cancer, the better the chances of prognosis are.
Hopefully, we have cleared all your queries about cervical cancer. Take necessary precautions and stay safe!
