Did you know around 65 million people around the world develop epilepsy in their life? Luckily most of them are cured. On the other hand, many epileptic patients have to be dependent on lifelong medications.
Epilepsy is a neurological condition resulting in loss of control of motor functions. The most common symptom of epilepsy is seizures.
Almost all of us know someone who is, or has been a patient of epilepsy once in their life. This shows how common this neurologic disorder is.
Now you may ask, is there any cure for epilepsy? And fortunately there is!
In fact, that’s the thing about diseases that are common worldwide, as the higher number of cases around the world make it useful for the researchers to collect facts about the disease. As the more the available data is, the easier it is to work on the treatment.
Now let’s highlight the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of epilepsy. Hopefully, all your queries will be cleared under this article. Let’s dive in!
What Is Epilepsy?
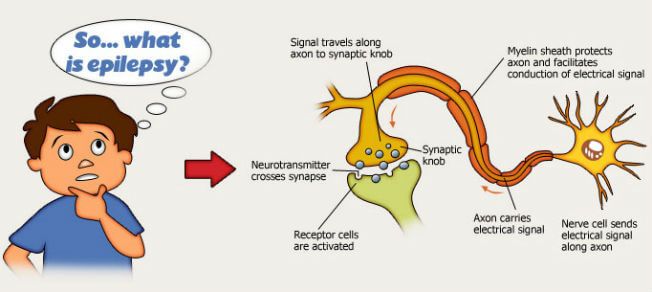
In simple words, epilepsy is a disorder that arises in the brain and produces mild to severe epileptic seizures throughout the body. It is caused by excessive discharge of neurons that disturb the normal mechanisms of the body.
Moreover, epilepsy affects people of all ages and genders. However, according to the stats, epilepsy mainly occurs in babies and older people in the developed world. Whereas, in developing countries, it commonly affects older children and adults.
Now, what should you do if you see someone having an epileptic seizure? Or what should you do if you are having one yourself?
Well, to know the cure, you need to know the symptoms first.
Epilepsy Signs and Symptoms
Before we proceed further, remember that signs and symptoms of epilepsy vary from person to person. Plus, the symptoms might be similar or different in each episode of seizure.
Moreover, we know that epilepsy involves the brain cells affecting their activity, so the symptoms that appear are usually related to the brain’s motor activity. These may include:
- Increase tone
- Epileptic seizure
- Blank staring
- Being oblivious of the surroundings
- Dizziness
- Neurologic symptoms like anxiety, depression, fear, etc.
The most common among these are epileptic seizures. And all the other symptoms occur along with different types of seizures.
Types of Seizures
Now because of the complex structure of the brain and its effect on the body, seizures are divided into two types:
Focal or Partial Seizures
Focal seizures, as the name implies, arises in a part of the brain. They have less serious symptoms than the generalized seizures (described later).
There are two further classifications of focal or partial seizures:
- Simple focal seizures: In this type of seizure, there is partial loss of body function without the loss of consciousness.
This means that the patient is fully aware of the surroundings but there can be variations in vision, smell, taste, and hearing abilities.
Moreover, focal jerky movements last for a brief period along with dizziness and tingling sensations.
- Complex focal seizures: This type of seizure occurs with impaired awareness that is with loss of consciousness.
As a result, the patient stares blankly in space, performs repetitive movements like chewing, hand rubbing, or doesn’t respond to the doctor’s commands.
Generalized Seizures
Unlike partial seizures, generalized seizures involve the whole brain. For a better understanding, the generalized seizures are divided into six types;
● Absence Seizures:
Absence seizures are the non-motor type of generalized seizures. They are also known as petit mal seizures. In this type of seizure, there is a brief loss of consciousness, usually affecting the children.
As a result of the neuronal disruption, the patient stares blankly in the space. Plus, due to repetitive movements, there would be lip-smacking and eye blinking.
● Tonic Seizures:
The term tonic arose from the tone. Muscle tone is the normal resting state of the muscle, that is when we are not using a muscle the continuous contraction in that tissue is its tone.
Now in tonic seizures, this muscle tone is greatly increased due to disrupted neuronal activity. As a result, the muscle becomes stiff. Mostly back, arm and leg muscles are affected.
It mostly affects both sides of the body and lasts for less than 20 seconds. For example, if there are tonic seizures in the legs, the patient falls on the ground due to tonic contraction of muscles.
● Atonic Seizures:
As opposed to tonic seizures, Atonic seizures occur due to the loss of muscle tone. They are also known as drop or akinetic seizures.
In this type of seizure, the patient has episodes of falling on the ground (drop attacks) due to the relaxing of muscles. If these seizures occur in the neck, the patient will have a noticeable head drop.
● Clonic Seizures:
Clonus means repetitive contraction and relaxation of the muscles. It either arises in the whole body or certain parts, mainly the face, neck, and arm.
In clonic seizures, there are jerky or rhythmic movements of the muscle lasting for a few seconds to minutes. However, clonic seizures are rare as compared to tonic-clonic seizures.
● Myoclonic seizures:
These seizures are more or less similar to clonic seizures. In fact, at times, it becomes hard to differentiate between the two. However, one way to isolate myoclonic seizures is to note the period of their occurrence.
Myoclonic seizures are the brief jerky or twitching of the muscles lasting for not more than a second (unlike clonic seizures). They usually occur in eyelids, arms, or legs.
● Tonic-clonic Seizures:
As the name suggests, these types of seizures have properties of both tonic and clonic seizures.
Previously known as grand mal seizures, they are now commonly known as convulsions. These are the advanced types of seizures, in which the patient has a loss of consciousness, loss of bladder control, and muscle stiffness followed by jerking of the affected part.
They usually last for one to three minutes. But if lasting for more than that, urgently appoint a doctor.
Note: Not every seizure is due to epilepsy. Some non-epileptic seizures can also result from, high-grade fever, hypoglycemia, withdrawal symptoms, and head trauma.
Causes of Epilepsy
You will be surprised to know that in six out of ten patients, epilepsy arises from an unknown cause. However, in some cases, the cause can be determined.
Genetic Influence
People with no identifiable cause of epilepsy might have a genetic predisposition. Meaning, if your parents have epilepsy, your risk of getting it at some stage of life is two to five percent more than the people with non-epileptic genes.
Acquired
Some known causes of epilepsy include:
- Brain injury: Any moderate or severe injury to the brain due to head trauma in accidents can result in epilepsy.
- Diseases: Some infectious diseases like, AIDS, meningitis, Alzheimer’s, and even brain tumors can cause epilepsy.
- Prenatal injury: Prenatal means before birth. Infants are at higher risk of getting injured when in the womb. Epilepsy due to injury can be of any cause, may it be poor nutrition, decrease oxygen supply or infections in the brain.
Even though the occurrence of epilepsy is unrelated to age, there are a few diseases or conditions in certain age groups that can trigger epilepsy or epileptic seizures.
- Children: Around three out of ten children with autism have seizures. However, the exact cause is still not known.
- Young adults: In young people or teenagers, epilepsy is mostly caused by trauma to the head. This is because people at this age tend to be more active and so the risk of injury to the head is more common in this age group.
- In the elderly: Shock is the leading cause of epilepsy in older adults over the age of 35.
Epilepsy Diagnosis
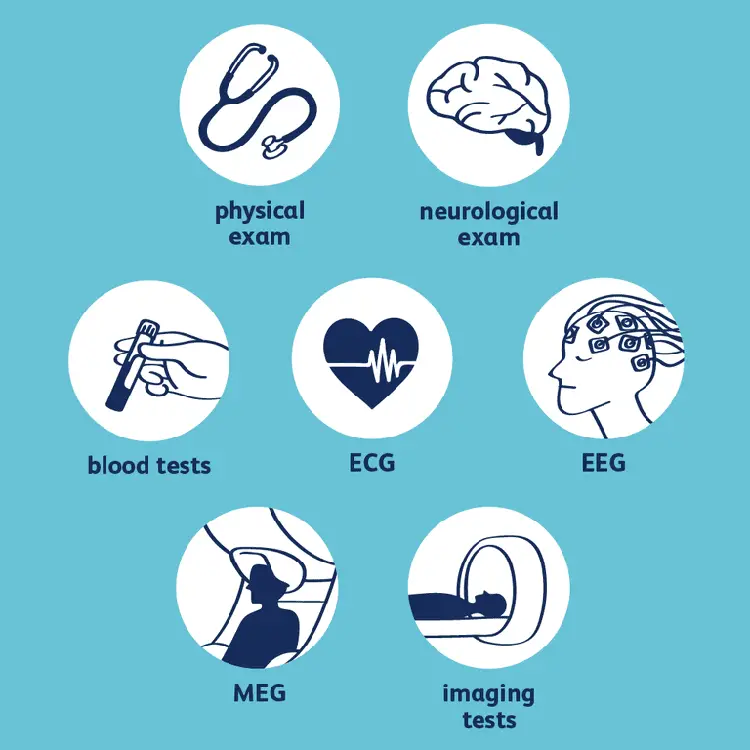
Though epilepsy is very common worldwide, not everyone knows about it in detail. But if it is misdiagnosed, you might have to suffer from future complications.
So, if you are having repetitive seizures, even if they are mild, consult with a doctor to get early treatment.
Quick Tip: Make an epileptic journal (or ask someone close) to keep a record of your symptoms. Write the date and day when you had a seizure then recall your activities of that day and note them down. If another episode of seizure takes place, write and compare it with the previous episode. Your journal can even help doctors to treat epilepsy.
To diagnose the possibility of epilepsy, your doctor will take your family history, and check your mental and motor functions. Further tests to detect the exact cause of seizures are as follows:
Neurological tests
While you give your general history to the doctor, the doctor will observe you head-to-toe for any abnormal neurologic signs.
The first step toward diagnosis is a neurological examination. You will be checked for any unusual mental or physical functioning to find out the type of epilepsy or seizures you have.
Blood tests
Complete Blood Count helps in diagnosing any internal infections that have a risk of spreading to the brain. This helps in determining the drug of choice that can be given without any disease-associated side effects.
EEG
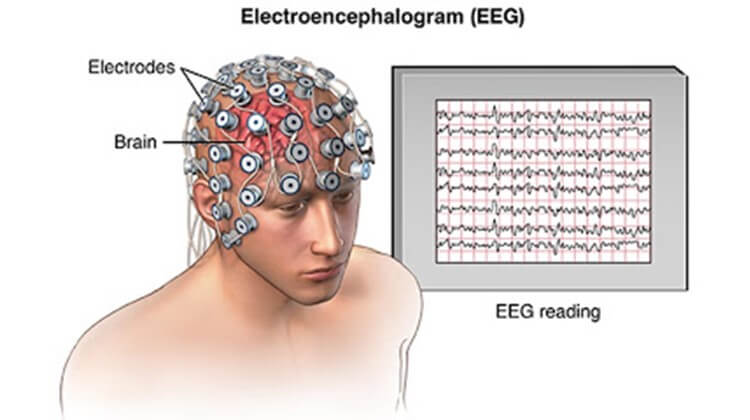
The most common way to find out about epilepsy is EEG testing. In EEG or Electroencephalogram, several electrodes are fixed on different areas of the scalp.
It detects any abnormal brain activity and displays them on screen as brain waves. It can be done while you are asleep or awake independent of whether you are having seizures during the process or not.
Plus it can even rule out the possibility of non-epileptic seizures, as in these patients, there are no findings in EEG.
In High-density EEG, the electrodes are placed more closely to determine the exact area of the brain that is affected.
CT scan
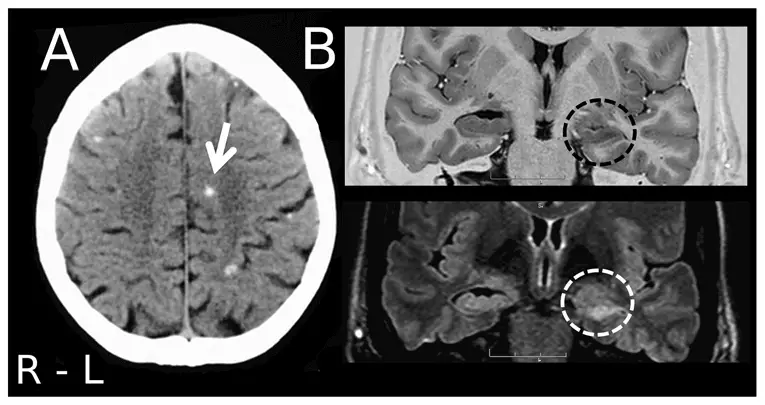
Computerized Tomography (CT scan) provides better and more detailed imaging of the brain. It determines the cause of the seizure, like, hemorrhage, cysts, or tumors by using high-energy X-rays.
MRI
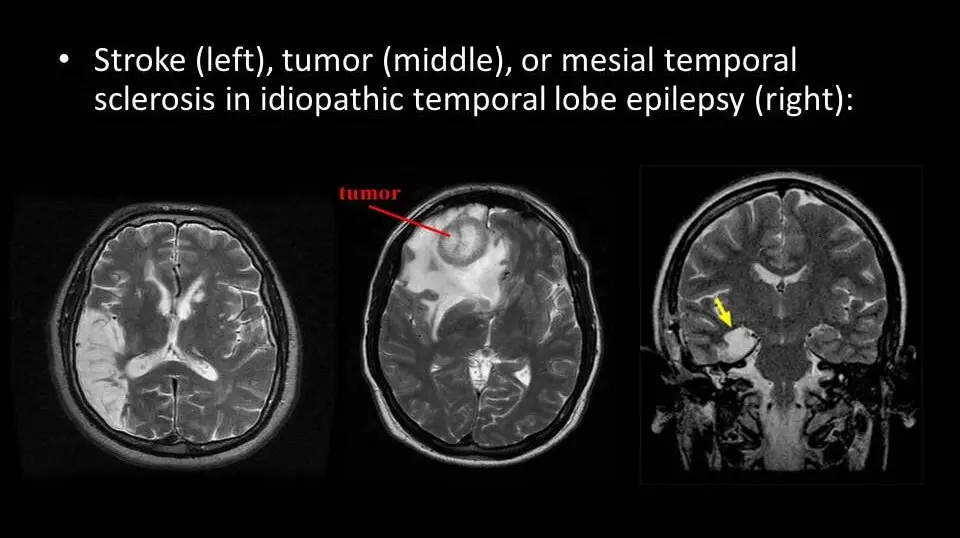
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI scan) is another imaging technique useful in identifying lesions in the small areas of the brain. It uses magnetic radiation and creates a clear 3-D image for accurate detection of the affected part.
PET scan
In PET or Positron Emission Tomography, a low-dose radioactive tracer is injected into the veins that reach the brain via blood. This helps in detecting the brain lesions that are visible as bright spots on the PET scan.
Related: Seizure-detection Device for Epilepsy – How Does it Work?
Living with Epilepsy
The life of epileptic patients is not easy. There is a constant struggle of hiding the seizures. Some people go into severe depression, acquire suicidal thoughts, and face difficulty in socializing.
Children
The children who have epilepsy have a low IQ level and they tend to memorize things slower than the rest of the children. This is why these children can have behavioral changes as well and become easily irritable.
However, these changes occur in almost every type of neurologic disorder. And in around 15 to 35% of cases, it arises due to epilepsy.
Adults
On the other hand, around 30 to 70% of adult epileptic patients have mood changes and fall into severe depression. They also become stressed about small things and don’t know how to respond intellectually.
Epilepsy Treatment
The primary treatment for epilepsy is epileptic medication. In case the medications aren’t fruitful, surgery or certain types of therapies have to be done.
Anti-seizure Medications
Anti-epileptic drugs are the standard choice to treat epileptic seizures. However, these drugs do not cure epilepsy. The aim is to control the frequency and occurrence of symptoms.
Several medicines for epilepsy vanish the symptoms of epilepsy giving patients a chance to live a seizure-free life after two years or more.
The anti-epileptic drugs are taken once or twice a day depending on how severe the symptoms are.
Plus, your doctor will tell you about the daily intake, as well as, when to discontinue the medicine according to the severity, and intensity of symptoms.
However, there is no drug without a side effect. Following are the side effects that can occur during the treatment.
- Laziness
- Weight gain
- Nausea
- Allergic rashes
- Bone weakness
- Loss of coordination
- Difficulty to think, speak and memorize.
In severe and rare cases, that is, when you don’t stop the drug intake at the right time, the following side effects can occur:
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts
- Inflamed liver
- Hyperactivity and irritability
Surgery
When there are no satisfactory results of drugs, your doctor might suggest a surgical treatment of the affected site. The goal of any surgery is to remove the lesion from the root and stop the severity of symptoms.
Resection is the method performed to decrease the number of seizures. The term resection simply means to take out the part or lobe of the brain that is causing seizures.
In most cases, temporal lobectomy is done, in which the surgeon removes the temporal lobe to prevent further episodes of seizures.
Note: Temporal resection is only done if the temporal lobe of the brain is affected. If some other part is involved there would be the resection of that part only.
Therapeutic Procedures
These are the alternatives to drug and surgical treatments. The therapeutic procedures help in reducing the seizures either by vagal nerve or deep brain stimulation or by taking a ketogenic diet.
Complications of Epilepsy
There are a few complications that may occur in some patients. Mostly these complications are related to the activities that require intense focus. Following are the complications of epilepsy:
- Injury: Due to the tonic-clonic seizures that can occur any time, you might fall suddenly and lose control over your body.
- Driving: Driving is affected and your doctor might not allow you to drive until you are fully recovered to avoid any accidents.
- Systemic complications include: pulmonary distress, cardiac arrest, metabolic disturbances, or brain dysfunction including relapsing seizures.
- Complications related to surgery are common. There may be an infection, bleeding after months or years, and trauma to the brain that is a hospital emergency.
Other complications include severe depression, drowning, allergic reactions to the drugs, and death.
FAQs
Different people have different triggers. For example, some people get triggered by a flashing light, while others don’t. Some of the commonly reported triggers are:
● Sleep deprivation
● Stress
●Hormonal disbalance
● Caffeine
● Alcohol
● Eating habits
Some people go through a status epilepticus attack. During this attack, the patient fails to regain consciousness in between the seizures. And these seizure attacks last for five minutes requiring medical emergency.
Other long-term side effects are either related to some medications, memory, infertility, or sudden death occurs.
Conclusion
So to sum it up, epilepsy is a disorder of the brain that can occur due to brain lesions leading to different types of seizures.
No matter if it’s your first time getting seizures, you should consult a doctor if you notice any strange movement in the body. Do not wait for another!
Hopefully, we have answered all your questions, and there isn’t any confusion regarding epilepsy.
